The Ultimate Guide to Achieving Your Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) Certification
Entering the healthcare industry as a medical assistant offers numerous rewarding opportunities. Obtaining the Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) credential is a strategic step that enhances your employability, broadens your clinical and administrative skills, and opens pathways to a thriving career. This comprehensive guide covers every aspect of becoming an RMA, from eligibility requirements and certification processes to job prospects and ongoing recertification obligations.
Understanding the Role of a Registered Medical Assistant
A registered medical assistant is a healthcare professional who has successfully passed the RMA certification exam administered by the American Medical Technologists (AMT). These professionals are vital in healthcare settings such as clinics, hospitals, outpatient centers, and medical offices, where they handle both clinical procedures and administrative responsibilities. RMAs are trained to perform a variety of tasks, including patient care, record-keeping, and medical billing, making them versatile contributors to medical teams.
The role of a medical assistant is evolving rapidly, especially with technological advancements like electronic health records (EHR/EMR systems) and telehealth services. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, for example, is transforming operational workflows and decision-making processes. For deeper insights into these technological impacts, explore how AI influences healthcare.
How to Become a Registered Medical Assistant
Embarking on the journey toward RMA certification involves several key steps. First, aspiring candidates must verify their eligibility through one of the recognized pathways. Once eligible, they can apply for the certification exam, prepare diligently, and schedule their test at an authorized testing center.
Applicants can choose to take the exam either at their educational institution if it offers testing services or at a nearby Pearson VUE testing center, which provides convenient locations nationwide. On exam day, candidates must present valid identification, such as a driver’s license or passport, to verify their identity.
Candidates should familiarize themselves with the exam syllabus and allocate sufficient time for preparation. Many resources, including study guides and practice tests, are available to enhance readiness. Successful completion of the exam confirms your status as an RMA and opens the door to diverse employment opportunities.
Eligibility Paths for Certification
To qualify for the RMA exam, applicants must meet at least one of the following criteria:
-
Educational Path: Graduates from an accredited medical assisting program within the last four years, which includes at least 720 clock hours of coursework and 160 hours of externship experience.
-
Work Experience Route: High school graduates with five years of full-time medical assisting experience under a licensed physician, alongside current CPR certification.
-
Military Route: Individuals who have completed a U.S. Armed Forces medical training program within the past four years.
-
Instructor Route: Current instructors of accredited medical assisting programs with more than five years of full-time teaching experience.
For detailed information on eligible training programs and requirements, visit the official AMT certification guidelines.
Benefits of Becoming a Registered Medical Assistant
Choosing to earn the RMA credential offers several significant advantages:
-
Minimal Educational Barriers: Unlike some healthcare roles, becoming an RMA does not necessarily require prior enrollment in a medical assisting degree program. Certification can be achieved through recognized training and experience, reducing the barrier to entry.
-
Diverse Job Settings: RMAs can work in a variety of healthcare environments, such as outpatient clinics, hospitals, specialty departments like pediatrics or gynecology, and even administrative offices. This flexibility allows professionals to tailor their careers to their interests.
-
Enhanced Employability and Less Competition: Credentialed RMAs are often preferred by employers because they can perform a broader scope of services legally permitted by law, giving candidates a competitive edge.
-
Growing Demand: The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 14% growth in medical assistant employment from 2022 to 2032, indicating a robust job market. Employment is expected to increase from approximately 764,400 to 872,900 positions, reflecting the expanding healthcare needs of an aging population.
-
Work Flexibility: Medical assistants benefit from more predictable and flexible hours compared to other healthcare providers, many of whom work unpredictable or shift-based schedules.
Educational and Training Requirements
Formal Education
Applicants must have graduated from an accredited medical assisting program within the past four years. The program should include at least 720 hours of coursework and 160 hours of externship experience, all verified through official transcripts. Accreditation must be granted by an agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education, ensuring quality and standardization.
On-the-Job Training
For those with relevant work experience, eligibility requires full-time employment as a medical assistant within the last five years under a licensed physician or healthcare facility. Additionally, candidates must hold valid CPR certification from the American Heart Association or similar accredited organization. Submission of proof of employment, CPR certification, and a high school diploma is essential.
Certification Application Process
Once eligibility is confirmed, candidates can apply online for the exam, schedule their test date, and prepare accordingly. On exam day, applicants are required to present a valid photo ID, such as a driver’s license or passport, to complete the verification process.
Interesting:
Essential Skills for a Successful RMA
The role demands a combination of administrative and clinical skills:
- Administrative Skills:
- Excellent communication abilities
- Knowledge of insurance procedures and regulations
- Ability to handle clinical emergencies effectively
- Proficiency with healthcare technology and electronic records
-
Empathy and patient rapport-building skills
-
Clinical Skills:
- Compassionate and positive attitude in stressful situations
- Proficiency with medical instruments and procedures
- Strict adherence to sanitation and infection control protocols
- Ability to administer injections and perform laboratory tasks
- Patient education regarding medications and treatments
Employers increasingly expect RMAs to be adept with electronic health records (EHR/EMR systems), telehealth support, and cross-training in procedures like phlebotomy and diagnostic testing. Continuous professional development ensures your skills remain current in this dynamic environment.
Comparing Registered Medical Assistant and Certified Medical Assistant
Both credentials are nationally recognized and highly valued within the healthcare sector. While they share many core competencies, there are notable differences:
| Aspect | Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) | Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) |
|———|————————————-|———————————–|
| Certifying Body | American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) | American Medical Technologists (AMT) |
| Eligibility Criteria | Graduation from a CAAHEP/ABHES-accredited program | Education, work experience, military training, or instructor route |
| Certification Renewal | Every 5 years, via exam retake or CEUs | Annually, via CCP or recertification exam |
| Exam Cost | Approximately $125 | Approximately $120 |
| Salary (Median) | Around $39,610 | Similar, about $39,119 |
| Recognition | Widely regarded as the “gold standard” | Recognized in many states with strong credentials |
Choosing between the two depends on your career aspirations, educational background, and personal circumstances. The CMA credential is often favored in larger hospitals and private practices, whereas RMA offers flexible eligibility options for diverse backgrounds.
Job Responsibilities and Daily Duties
Medical assistants are essential for ensuring smooth clinic operations and quality patient care. Their responsibilities include:
Administrative Tasks:
- Scheduling appointments and managing patient flow
- Communicating diagnosis and treatment plans to patients
- Verifying insurance coverage and processing claims
- Maintaining accurate medical records
- Operating office technology, such as EHR systems
Clinical Tasks:
- Measuring vital signs and recording patient history
- Assisting with examinations and procedures
- Performing blood draws and laboratory tests
- Preparing examination rooms and sterilizing instruments
- Providing patient education on medications and health instructions
The role requires meticulous attention to detail, compassion, and the ability to function effectively under pressure, especially in emergency situations. The need for precision and empathy underscores the importance of a well-rounded skill set.
Career Outlook and Growth Opportunities
The healthcare landscape is experiencing significant growth, with the BLS predicting a 16% increase in medical assistant employment from 2021 to 2031. This surge is driven by the expanding healthcare needs of the aging baby boomer population and the increasing complexity of medical services.
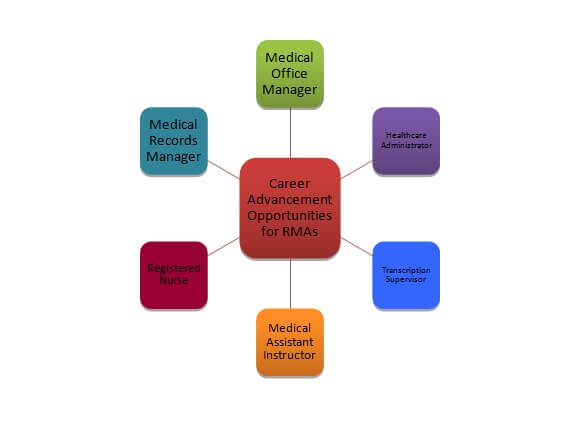
Registered medical assistants can specialize in various fields such as pediatrics, obstetrics, ophthalmology, or podiatry, depending on their interests. They may also advance into roles like healthcare administration, medical education, or even pursue further nursing qualifications.
Salary Expectations Across Healthcare Settings
| Industry Sector | Hourly Wage (Median) | Annual Wage (Median) |
|——————-|———————-|———————-|
| Physician Offices | $19.14 | $39,810 |
| Hospitals | $20.19 | $41,990 |
| Outpatient Centers | $22.75 | $47,320 |
| Educational Institutions | $20.70 | $43,050 |
These figures vary depending on geographic location, level of experience, and specific employer policies, but they reflect a healthy income potential for certified professionals.
Maintaining Certification: Recertification and Continuing Education
To uphold your RMA status, you must comply with recertification requirements, which include paying an annual fee of approximately $65 and fulfilling the Certification Continuation Program (CCP) obligations every three years. This involves earning 30 CCP points through activities such as continuing education, employment, and professional development.
Failing to meet these requirements necessitates retaking the certification exam, which incurs a fee of about $205. The process includes submitting documentation that verifies your ongoing participation in relevant activities, ensuring your skills and knowledge stay current in a rapidly evolving field.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Your Path in Medical Assistance
Deciding between the CMA (AAMA) and the RMA (AMT) certifications depends on your background, career goals, and employment preferences. The CMA is often regarded as the gold standard, especially in large hospitals, whereas the RMA offers flexible eligibility routes suitable for diverse educational and experiential backgrounds.
Both credentials validate core clinical and administrative competencies, opening doors to meaningful healthcare careers. Continual professional development and specialization can further enhance your prospects, making your role as a medical assistant both rewarding and sustainable.
For comprehensive information on healthcare systems worldwide, including comparisons of national healthcare quality, visit which country has the best healthcare system. Additionally, understanding the broader structure of healthcare delivery can provide context for your role and growth opportunities within this vital industry.
Written by: Casey Gardner
Casey Gardner combines extensive healthcare experience with a passion for education, having served as both a physician assistant and a medical assistant for over two decades. Her dedication to producing clear, informative content has helped countless aspiring healthcare professionals navigate their career paths successfully.





