Effective revenue cycle management (RCM) is vital for healthcare organizations striving for financial stability and operational excellence. As the industry evolves, driven by technological advancements and shifting reimbursement models, understanding how to optimize each step of the revenue cycle becomes increasingly important. This guide explores the critical components of RCM, highlights current best practices, and provides strategies to ensure your practice remains financially healthy in 2026 and beyond.
Healthcare providers face complex challenges in collecting payments accurately and efficiently. From preregistration to patient collections, each phase requires precise execution and adaptation to new tools such as automation, AI, and analytics. Proper management not only improves cash flow but also enhances patient satisfaction and compliance, positioning your organization for sustainable growth.
What is Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare?
Revenue cycle management encompasses the entire process of tracking and collecting revenue from patient encounters—from the initial appointment or hospital visit to the final payment. It begins with scheduling and registration and extends through claim submission, payment posting, and patient billing. The goal is to optimize revenue by minimizing errors, reducing denials, and accelerating reimbursements.
Unlike simple billing, RCM involves a strategic approach that integrates clinical documentation, financial policies, and technological tools to ensure maximum reimbursement while maintaining regulatory compliance. This integrated process impacts nearly every department, from front desk staff to billing specialists, and even clinical teams.
Why is RCM so crucial in today’s healthcare landscape?
- Emerging payment models like value-based care demand tighter integration between clinical outcomes and revenue.
- Advances in interoperability and artificial intelligence are transforming data flows and operational efficiencies.
- Leveraging analytics and automation minimizes manual errors, speeds up reimbursements, and enables early identification of financial risks.
- The U.S. healthcare system incurs approximately $262 billion annually due to inefficiencies in revenue cycle processes, according to the National Institutes of Health. This underscores the need for smarter, more agile RCM strategies.
Benefits of Effective Revenue Cycle Management
A robust revenue cycle not only ensures steady cash flow but also improves overall operational performance. When financial processes are streamlined, practices experience fewer billing surprises, staff can dedicate more time to patient care, and overall growth becomes attainable.
Modern practices utilize advanced tools such as AI-enabled coding, automated claim workflows, and real-time denial analytics to streamline revenue management. As the industry transitions toward value-based arrangements and increased data sharing, a proactive RCM approach helps practices stay ahead of these changes.
Key advantages include:
- Enhanced patient satisfaction: Transparent billing processes and timely communication foster trust.
- Faster cash flow: Accurate charge capture and clean claims lead to quicker reimbursements.
- Reduced claim rejections: Automated error detection prevents costly rework.
- Regulatory compliance: Consistent processes minimize audit risks.
- Operational scalability: Smooth workflows free staff to focus on strategic growth initiatives.
- Clinical staff relief: Less administrative burden allows providers to dedicate more time to patient care.
Optimizing these areas yields better financial outcomes, improved staff morale, and higher patient retention.
Webinar: Healthcare Practice Revenue Cycle 101
Learn more about how to optimize your practice’s revenue cycle through our comprehensive webinar, where Kathi Rennick discusses the essential processes, common pitfalls, and best practices for auditing and improving your revenue management system.
On-Demand Webinar Duration: 49:56
Speaker: Kathi Rennick, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CHC, Director, LBMC Physician Business Solutions, LLC
Recorded: February 9, 2021
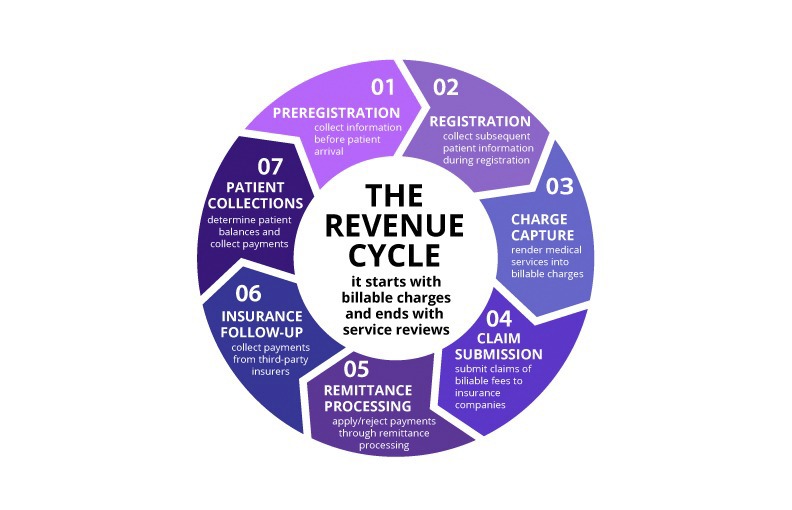
The 7 Critical Steps in Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management
Here’s a current overview of each phase, incorporating the latest strategies such as automation, payer complexity, and data analytics:
| Step | Purpose | Optimization Strategies |
|—|—|—|
| 1. Preregistration | Gather patient data, verify insurance, and assess coverage before the visit. | Utilize clearinghouse integrations for real-time eligibility checks, employ digital intake forms to improve accuracy, and prepare scripts to set expectations early. |
| 2. Registration | Confirm demographic and insurance details, collect copays, and secure authorizations. | Automate insurance verification workflows, implement electronic signatures, and maintain detailed audit trails for accuracy. |
| 3. Charge Capture | Accurately document and transfer all billable services. | Use EHR-integrated coding tools, automate charge entry, and perform regular audits to identify missing or miscoded charges. |
| 4. Claim Submission | Send well-prepared claims for reimbursement. | Deploy AI-driven claim scrubbing, monitor rejection trends, and automate claim routing through clearinghouses. |
| 5. Remittance Processing | Review payments, adjustments, and denials. | Automate remittance posting, utilize analytics to flag anomalies, and regularly review denials and write-offs for improvement. |
| 6. Insurance Follow-Up | Address unpaid claims and manage accounts receivable. | Prioritize follow-up using denial analytics, assign payers by expertise, and automate status tracking to speed resolution. |
| 7. Patient Collections | Collect patient responsibility amounts efficiently. | Offer online payment portals, automate statements, and send reminders via text or email to accelerate payments. |
Modern revenue cycle management leverages real-time data, automation, and patient-focused workflows. Practices adopting these innovations are better equipped to improve cash flow, minimize denials, and scale growth.
1. Preregistration
Preregistration is the pivotal first step. It involves collecting detailed patient information, verifying insurance eligibility, and assessing coverage before the appointment. Many practices now integrate digital platforms that allow real-time eligibility checks while the patient is still on the phone or online, speeding up the process and reducing manual errors. This process also offers an opportunity to discuss financial expectations, including co-payments and cancellation policies, setting a transparent tone for the encounter.
Implementing a comprehensive preregistration process helps prevent downstream issues such as claim denials due to incomplete or inaccurate information. Regularly reviewing and refining this step can significantly improve initial collections and overall cash flow.
2. Registration
Registration ensures the accuracy of patient details and insurance data. During this phase, providers confirm address, contact information, date of birth, guarantor details, and insurance benefits. Many organizations now use ID scanners and electronic signatures to automate verification and reduce manual entry errors.
Collecting co-payments upfront and verifying authorizations are critical to securing payments and avoiding claim rejections. Having integrated financial clearance tools helps staff track required documentation and authorization statuses in real-time, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and missed reimbursements.
3. Charge Capture
Charge capture involves recording all billable services accurately. This can be automated through EHR systems that transfer documentation directly into billing modules, or done manually by staff. AI-assisted coding tools are increasingly used to flag incomplete documentation and suggest correct codes, reducing missed charges.
Regular audits of charge capture processes help identify gaps, especially for ancillary services that are often overlooked. Ensuring charges are correctly documented and transferred is fundamental to capturing full revenue.
Interesting:
4. Claim Submission
Once charges are documented, claims are prepared and submitted to payers. The goal is to generate clean, accurate claims to facilitate prompt payment. Claim scrubbing software, often powered by AI, checks for common errors before submission, reducing rejection rates.
Claims are routed through clearinghouses, which handle the submission process. Monitoring transmission reports and rejection notices in real time allows billing teams to address issues swiftly, preventing delays and revenue leakage.
5. Remittance Processing
After submission, practices receive remittance advice detailing payments, adjustments, and denials. Proper review of these documents is essential. Electronic posting systems can automate much of this process, but regular oversight is necessary to catch errors or discrepancies.
Fee schedules should be reviewed annually to align with negotiated rates and market adjustments, ensuring providers are paid appropriately. Identifying and addressing avoidable write-offs resulting from process breakdowns can recover significant revenue.
6. Insurance Follow-Up
Persistent follow-up on unpaid or underpaid claims helps improve collections. Using denial analytics and payer-specific reports enables practices to prioritize claims that need attention, reducing aging receivables. Assigning follow-up responsibilities based on payer expertise and automating status updates streamline this process.
Efficient follow-up can recover revenue that might otherwise be lost, and proactive management reduces the risk of accounts becoming uncollectible.
7. Patient Collections
The final, often most challenging, step involves collecting patient-responsible balances. Collecting at the point of care remains the most effective approach. Training staff to explain financial responsibilities clearly and utilizing digital payment options expedites collections.
Automated statements, reminders via text or email, and self-service portals encourage prompt payments. Maintaining a regular statement cycle ensures ongoing cash flow and reduces the backlog of overdue accounts.
Revenue Cycle Management Services from LBMC
When revenue cycle processes falter, it affects cash flow, staff morale, and patient satisfaction. LBMC’s Healthcare Advisory team specializes in diagnosing weaknesses and implementing tailored solutions to improve operational efficiency, reduce claim denials, and enhance revenue collection.
Our firm helps healthcare organizations identify operational gaps, optimize workflows, and leverage innovative tools. We support practices nationwide, offering both on-site and remote consulting tailored to your specific needs.
If you seek to strengthen your financial operations and ensure timely payments, explore our comprehensive revenue cycle management services.
Webinar: Applying AI and Automation in Revenue Cycle Management
Discover how emerging technologies like generative AI are transforming revenue cycle workflows. Our on-demand webinar features real-world applications and expert insights that can help your practice stay competitive.
FAQs about Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
How does revenue cycle management work in healthcare?
RCM encompasses all steps from scheduling and registration to collections. It integrates clinical, administrative, and financial processes to maximize revenue, minimize errors, and improve cash flow.
How does RCM differ from medical billing?
Medical billing is a component of RCM focused specifically on submitting claims and processing payments. RCM extends beyond billing to include patient registration, charge capture, denial management, compliance, and financial reporting.
What are common challenges faced by healthcare providers in managing revenue cycles?
Challenges include claim denials, delays in follow-up, inaccurate charge capture, inefficient workflows, staffing shortages, and adapting to changing payer rules.
Which key performance indicators should organizations monitor?
Important metrics include days in accounts receivable (A/R), denial rate, percentage of clean claims, net collection rate, and patient payment rates at point of service.
How can automation and AI enhance revenue cycle management?
Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up routine tasks, while AI tools can identify coding mistakes, predict potential denials, and prioritize claims for follow-up, leading to faster, more accurate reimbursements.
What services does LBMC provide for healthcare RCM?
LBMC offers comprehensive support, including process analysis, denial management, charge audits, staff training, and strategic planning—all designed to optimize your revenue cycle and support your mission.
For more insights on healthcare system development, visit key insights into Perú’s healthcare system and its development.