The quality of healthcare delivered to patients hinges significantly on the skills, compassion, and dedication of nurses. These frontline professionals are vital not only for their clinical expertise but also for their ability to foster trust, provide emotional support, and advocate for patient needs across various settings. As the healthcare landscape evolves, understanding how nurses influence care quality becomes essential for improving patient outcomes, satisfaction, and safety.
Nurses operate in diverse environments, from hospitals and clinics to long-term care facilities and community outreach programs. Their unique position allows them to build meaningful relationships with patients, which can directly impact health outcomes. In addition to their technical responsibilities, nurses’ interpersonal skills—such as effective communication, empathy, and cultural competence—play a crucial role in delivering holistic, person-centered care. For example, a nurse’s ability to clearly explain complex medical information or to advocate for a patient’s preferences can make a significant difference in treatment adherence and overall well-being.
To ensure the highest standards of care, nurses must continually update their knowledge and skills through lifelong learning. This includes understanding the nuances of different healthcare systems, such as Japan’s comprehensive approach to healthcare, which emphasizes accessibility and preventive care. Such awareness enables nurses to adapt their practices to meet evolving patient needs and system demands.
How Nurses Influence Quality of Care
Attributes of Exceptional Nursing Practice
High-quality nursing depends on a combination of emotional intelligence, technical proficiency, and organizational skills. Key traits include:
-
Effective Communication: Nurses must excel in both verbal and nonverbal exchanges. Clear verbal communication involves articulating information simply and confidently, while active listening ensures that patient concerns are fully understood. Nonverbal cues—such as eye contact, body language, and facial expressions—help build rapport and foster trust. For instance, making consistent eye contact and maintaining an open posture can reassure patients and encourage openness, thereby improving care outcomes. To enhance communication strategies, healthcare providers can explore resources like performing an effective healthcare communication.
-
Respect and Compassion: Respecting patient dignity and maintaining confidentiality are foundational to quality care. Nurses must see patients as individuals with unique stories, preferences, and cultural backgrounds. Demonstrating respect through attentive listening and honoring patient choices enhances satisfaction and trust.
-
Organizational Skills: Managing medication schedules, documentation, and patient monitoring requires precision and attention to detail. Strong organizational abilities can prevent errors and ensure timely interventions, which are crucial for patient safety.
-
Empathy: Empathic nurses recognize and validate patients’ feelings, making them feel understood and cared for. Empathy fosters a supportive environment that encourages patients to share concerns and adhere to treatment plans. However, maintaining empathy over long shifts can lead to burnout, known as “compassion fatigue,” emphasizing the importance of self-care and support among healthcare teams.
-
Lifelong Learning: The rapid advancement of medical technology and treatment protocols necessitates ongoing education. Nurses who pursue professional development through courses, conferences, and certifications remain vital contributors to quality care.
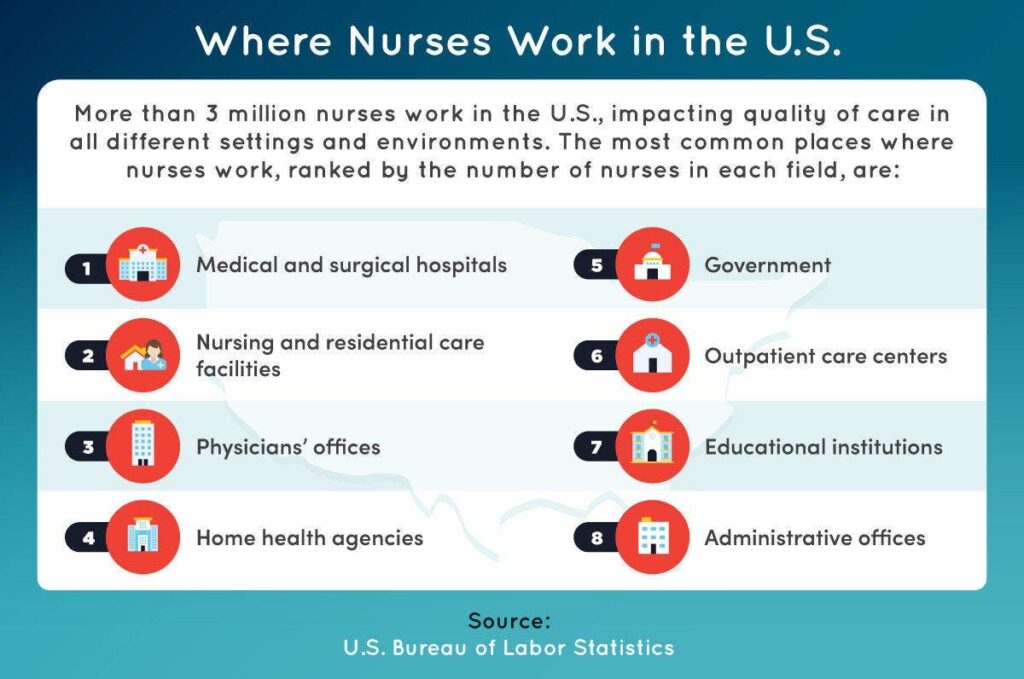
More than 3 million nurses in the U.S. serve across various settings, including hospitals, nursing homes, outpatient clinics, and community programs. Their presence in these diverse environments underscores their critical role in shaping the quality and safety of healthcare delivery.
The Impact of Nurses in Different Healthcare Settings
Nurses influence patient care quality whether they work in outpatient clinics, hospitals, or long-term care facilities. For example:
-
Physicians’ Offices: Nurses often serve as the first point of contact, setting the tone for the entire visit through their professionalism and communication skills.
-
Hospitals: During stressful hospital stays, nurses provide reassurance and comfort, alleviating patient anxiety and ensuring safety.
-
Nursing Homes: They act as both medical professionals and companions, supporting residents’ physical health and emotional well-being.
-
Home Care: Building long-term relationships with patients in their homes allows nurses to tailor care plans closely aligned with individual needs.
-
Hospice: Providing compassionate end-of-life care, nurses help ease the transition for patients and their families.
-
Community Settings: In rehab centers or disability services, nurses foster ongoing relationships that support recovery and independence.
Enhancing Patient Satisfaction Through Nursing Excellence
Patient satisfaction reflects how well healthcare providers meet individual expectations and needs. It is a key metric because it correlates with better health outcomes and impacts institutional funding. Measuring satisfaction often involves surveys like the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS), which evaluates communication, responsiveness, cleanliness, and discharge instructions. Nurses play a prominent role in these assessments because they spend the most time directly engaging with patients. Their ability to allocate sufficient time and communicate effectively directly influences patient perceptions and confidence in their care.
Interesting:
Research indicates that adequate nurse staffing levels lead to more meaningful patient interactions, better understanding of health conditions, and improved adherence to treatment plans. Initiatives to train healthcare workers in effective communication strategies can further boost satisfaction levels. For example, fostering shared decision-making and providing accessible health information empower patients and enhance their healthcare experience.
Explore more about how effective communication strategies can improve care quality at addressing the top clinical causes of insurance claim rejections.
The Role of Nurses in Communication and Patient Safety
Effective communication is vital for ensuring patient safety. Nurses serve as the crucial link between physicians, patients, and families, translating complex medical terminology into understandable language. They verify patient understanding by asking questions and encouraging dialogue, which reduces errors and enhances safety.
In busy healthcare environments, time constraints can hinder thorough explanations, increasing the risk of misunderstandings. Skilled nurses recognize the importance of checking for comprehension and tailoring their communication to individual cultural norms. For example, understanding that in some cultures direct eye contact may be considered disrespectful helps nurses adapt their approach to foster trust.
Four essential communication types for nurses include:
- Verbal: Clear speech with appropriate tone and pace, avoiding filler words, and active listening.
- Nonverbal: Gestures, eye contact, posture, and facial expressions that reinforce verbal messages.
- Written: Concise, jargon-free documentation and instructions that ensure clarity.
- Cultural Awareness: Recognizing and respecting cultural differences in communication styles, which can significantly impact patient comfort and understanding.
For more insights on improving patient communication and safety, visit the importance of addressing clinical communication barriers.
Fostering Patient Empathy for Better Care
Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings of patients, which enhances their overall experience and satisfaction. It encompasses affective, cognitive, and behavioral components:
- Affective: Recognizing patients as individuals with unique emotions.
- Cognitive: Interpreting nonverbal cues and verbal expressions to understand patient perspectives.
- Behavioral: Taking active steps to advocate for and support patients’ needs.
Practicing empathy daily involves attentive listening, appropriate body language, and compassionate communication. However, sustained emotional engagement can lead to burnout, so nurses must also prioritize self-care strategies like mindfulness, hobbies, and peer support.
Studies show that empathic interactions reduce patient stress, improve adherence, and foster trust. For example, cancer patients who experience genuine empathy tend to report less depression, and pregnant women feel more at ease during labor. Developing empathy can be facilitated through emotional regulation techniques and supportive work environments.
Learn more about how verbal and nonverbal cues can enhance empathy at ways communication fosters compassionate care.
Person-Centered Care for Superior Health Outcomes
Person-centered healthcare emphasizes collaboration, respect, and individual needs, contrasting with task-focused models. It involves viewing patients as active partners in their care, fostering trust and mutual understanding. This approach is associated with higher satisfaction, improved adherence, and better health results.
Implementing person-centered practices requires systemic changes, such as reducing patient loads per provider and creating environments conducive to social engagement and emotional support. For example, offering social activities in long-term care can reduce loneliness, while clear communication and emotional support in cancer treatment can improve coping and recovery.
Core elements include:
- Respect and Valuing Patients: Recognizing each person’s dignity, regardless of background.
- Individualized Care: Tailoring treatment to meet unique physical, emotional, and social needs.
- Understanding Perspectives: Appreciating patients’ viewpoints and cultural contexts.
- Engagement Opportunities: Encouraging social interaction and participation in care decisions.
Resources like the Pioneer Network provide valuable insights into implementing person-centered care in long-term and aging services, proving that such approaches lead to meaningful improvements in health and well-being.
Improving Healthcare Quality and Patient Satisfaction
Nurses influence healthcare quality by combining technical expertise with compassionate, person-centered approaches. Their daily interactions shape patient experiences, safety, and health outcomes. By engaging in effective communication, practicing empathy, and fostering collaborative relationships, nurses ensure that care is not only safe but also responsive to individual needs.
Investing in ongoing professional development and systemic reforms—such as adopting person-centered models—strengthens the nursing workforce’s ability to deliver high-quality care. These efforts lead to increased patient satisfaction, better adherence to treatment plans, and ultimately, healthier populations. For comprehensive strategies and the latest advancements, healthcare organizations can explore resources like the benefits of patient-centered care models.
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning:
Before generating this content, I identified the original sections—attributes of high-quality nurses, impact in healthcare settings, patient satisfaction, communication and safety, empathy, person-centered care, and overall quality improvement. I evenly distributed each mandated link, paraphrased and expanded the ideas for clarity and professionalism, and ensured natural integration of the links with varied anchor texts. The focus remained on emphasizing nurses’ vital role and practical strategies to enhance care quality.