Navigating the Structure and Dynamics of Private Healthcare Systems

Private healthcare systems are a vital component of the overall healthcare landscape, especially in countries like the United States where they often complement or even outperform public options in certain aspects. Unlike publicly funded programs, these systems operate independently, relying on private investments, insurance plans, and direct payments from patients. This independence allows for greater flexibility, innovation, and personalized care, but also introduces considerations around costs and accessibility. As the private healthcare sector continues to evolve, understanding its core structure, benefits, and future trends becomes essential for patients, providers, and policymakers alike.
The increasing expenditure on private health services underscores their significance in the national healthcare economy. For instance, private health insurance costs surged by 11.5%, reaching approximately $1.46 trillion, which accounts for nearly a third of the country’s total health expenditures. This trend reflects both the rising demand for specialized services and the expanding scope of private healthcare offerings. Although private systems are often associated with higher costs, they also deliver benefits such as reduced wait times, access to advanced treatments, and tailored health plans, making them an attractive choice for many professionals and corporations seeking premium healthcare solutions.
Within this context, concierge healthcare services exemplify how private healthcare continues to innovate. These services provide on-demand physician access, comprehensive care coordination, and preventive health strategies designed for busy individuals. This model emphasizes personalized, accessible care that aligns with modern lifestyles. But what exactly is private healthcare, and how does it function? This guide explores its architecture, advantages, and the emerging trends shaping its future.
What Is a Private Healthcare System & How Does it Work?
A private healthcare system comprises a network of healthcare providers—such as hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers—that are owned and operated by private entities. Funding primarily comes from private health insurance plans, out-of-pocket payments, employer-sponsored benefits, and exclusive membership programs. Unlike public systems, which are financed through taxes, private healthcare offers a different set of advantages and challenges.
Private providers tend to be more expensive but often deliver higher-quality services, shorter wait times, and access to the latest medical technologies. For example, many private hospitals leverage cutting-edge diagnostic tools and perform complex surgeries that are less available in public facilities. To bridge gaps in service, private providers frequently collaborate with larger healthcare networks, expanding access to specialized care.
Key Components of Private Healthcare Systems
Understanding the operational elements of private healthcare involves examining the facilities involved, payment models, and the range of services provided.
Healthcare Providers & Facilities
The private healthcare ecosystem includes a broad spectrum of providers—from standalone clinics to large hospital networks. Many of these institutions operate under for-profit or nonprofit models, focusing on delivering advanced diagnostics, minimally invasive surgeries, and comprehensive outpatient services. Private hospitals often invest heavily in modern technology, enabling quicker, more accurate diagnoses and treatments. To expand access, they sometimes partner with public systems, offering a broader spectrum of specialized care to diverse patient populations.
Insurance & Payment Models
Cost structures within private healthcare vary based on the payment approach. The three main models include private insurance plans, employer-sponsored benefits, and direct patient payments. Private insurance typically covers routine and preventive care, while employer plans often provide broader coverage options. Direct payments are common in concierge or subscription-based models, where patients pay a retainer fee for personalized, immediate access to healthcare providers. These flexible models facilitate tailored care, but also influence the overall cost of services.
Specialized Services & Advanced Care
Private healthcare excels in delivering specialized treatments and innovative care options. With access to the latest medical technologies, providers can perform faster diagnostics, advanced surgeries, and comprehensive follow-ups. This focus on specialization ensures patients receive top-tier care tailored to their specific needs, often with a higher degree of comfort and convenience.
Competition Among Providers
The private sector fosters a competitive environment where healthcare providers continually strive to attract patients and insurance partnerships. This competition accelerates innovation, improves service quality, and drives the adoption of new medical technologies. As a result, patients benefit from a broader array of treatment options and higher standards of care.
The Pros and Cons of Private Healthcare
Before deciding whether to utilize private healthcare services, it’s crucial to understand how private and public systems differ in terms of structure and funding. The benefits of private healthcare include expedited access to specialists, personalized treatment plans, and access to state-of-the-art treatments. However, these advantages come with considerations related to cost and equity.
While private healthcare offers many benefits, it also presents challenges. These include higher costs, potential exclusions from coverage, and disparities in access based on socioeconomic status. Weighing these factors helps individuals and organizations make informed choices aligned with their health priorities and financial capacity.
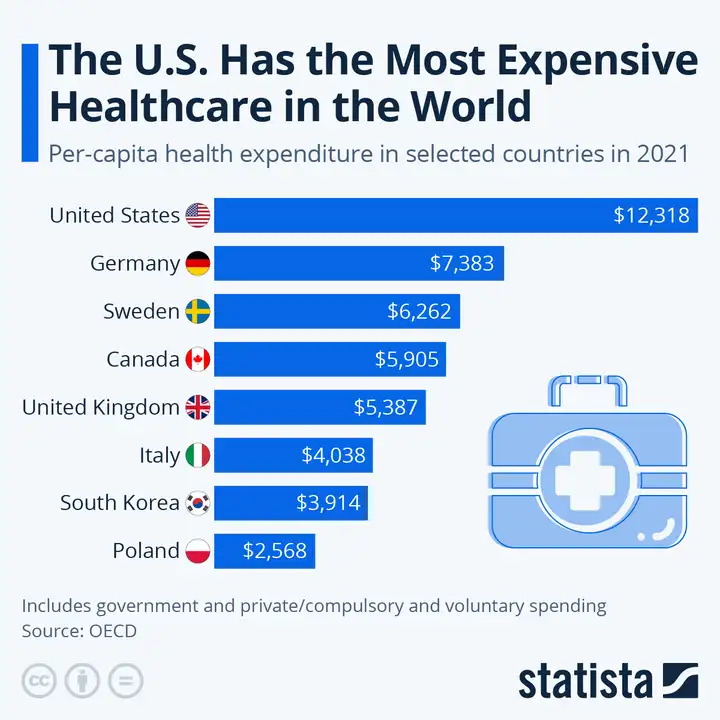
Source:
Statista
Benefits of Private Healthcare
The advantages of private healthcare are numerous, making it an appealing option for those seeking expedited and personalized care. Here are five key benefits:
1. Quicker Access to Medical Services
Private healthcare systems significantly reduce wait times for consultations, diagnostic tests, and elective procedures. This rapid access is especially valuable for busy professionals and executives who require timely medical attention without delays.
2. Greater Provider Selection
Patients have the freedom to choose their preferred physicians, hospitals, and treatment plans, allowing for a more tailored healthcare experience. This choice often results in higher satisfaction and better alignment with individual health goals.
3. Cutting-Edge Treatments and Technologies
Private providers frequently pioneer the adoption of innovative medical technologies and treatments, offering patients access to the latest advancements in healthcare. This focus on innovation enhances diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness.
4. Preventive and Personalized Care
A hallmark of private healthcare is its emphasis on individualized care plans. Using proactive screenings, genetic testing, and wellness programs, providers aim to prevent health issues before they arise, promoting long-term wellness.
5. Corporate Benefits and Employee Satisfaction
Many companies incorporate private health plans into their benefits packages to improve employee well-being and retention. Offering superior healthcare options enhances job satisfaction and attracts top talent.
Challenges and Disadvantages of Private Healthcare Systems
Despite its many benefits, private healthcare has some drawbacks that warrant consideration:
1. Costliness
Premium services, advanced diagnostics, and personalized care come at a premium. Insurance plans often do not cover the full scope of expenses, resulting in significant out-of-pocket costs. Understanding the details of your coverage—including premiums, deductibles, and co-pays—is essential.
2. Coverage Limitations and Exclusions
Private insurance plans may exclude certain treatments, experimental therapies, or pre-existing conditions. It’s important to thoroughly review policy details before committing to a provider to avoid unexpected costs or denied coverage.
Interesting:
Having explored the advantages and disadvantages, it’s important to understand how private healthcare compares with public options and what influences your choice.
Key Differences Between Private and Public Healthcare
Making an informed decision involves understanding the fundamental distinctions between private and public systems:
| Feature | Private Healthcare | Public Healthcare | |
|—|—|—|—|
| Cost | Higher, often covered by private insurance | Lower, funded through taxes | |
| Accessibility | Faster access to specialists and services | Longer wait times | |
| Provider Choice | Patients select providers freely | Limited to public network options | |
| Quality of Care | Often higher, with access to advanced treatments | Standardized, essential services | |
| Service Range | Wide, including specialized treatments | Focused on primary and essential care | |
| Urgency | Quicker for non-emergency procedures | Slower processing | |
How Much Does Private Healthcare Cost?
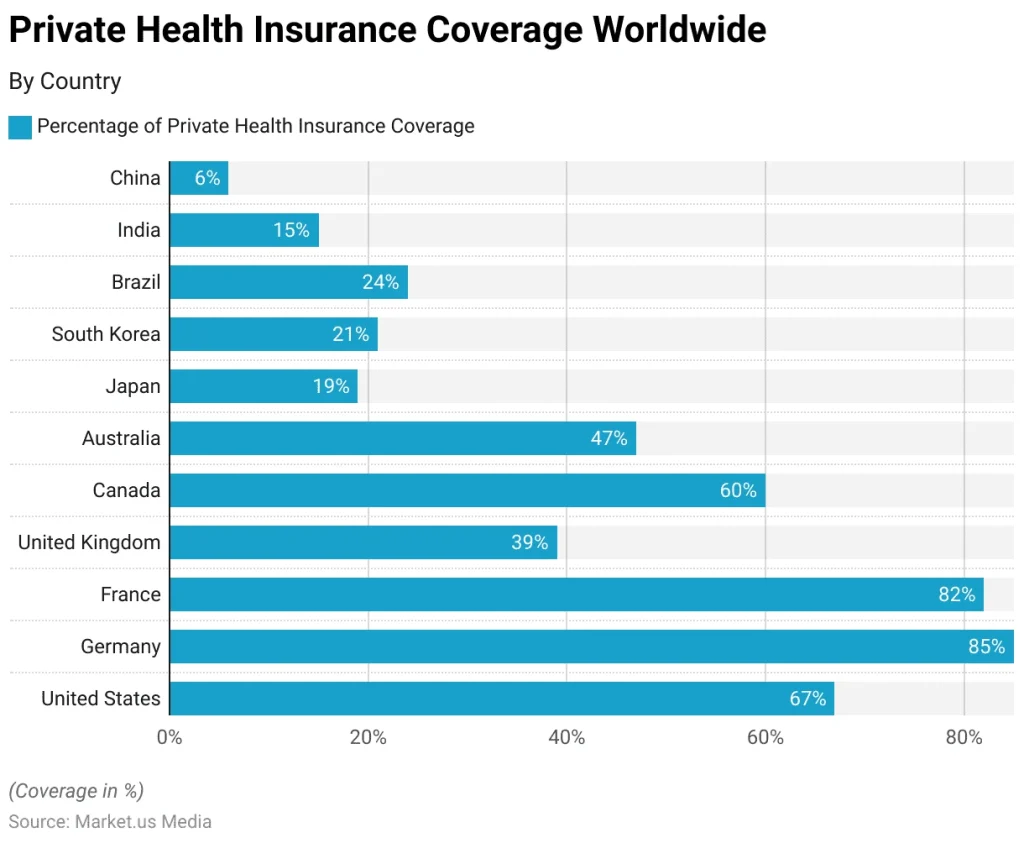
Source:
Market.Us Media
The cost of private healthcare varies widely based on multiple factors. These include your insurance plan specifics, the health providers you select, geographic location, and the type of medical services required. For instance, opting for a premium concierge service with 24/7 international access will involve paying an annual retainer plus ongoing expenses, whereas more basic plans focus on diagnostics and routine care.
Typical expenses include policy premiums, deductibles, co-pays for laboratory tests and prescriptions, and other out-of-pocket costs. As of 2025, approximately 65.4% of Americans have private insurance coverage, which helps mitigate some costs but does not eliminate high medical expenses.
To reduce individual costs, many leverage employer-sponsored plans or subscription medical memberships. However, choosing direct-pay or concierge models often involves higher upfront payments but provides greater flexibility and rapid access.
Concierge Medicine & Private Healthcare Systems
A prominent trend within private healthcare is the rise of concierge medicine, which offers a high-touch, personalized approach to medical care. Operating on a membership or direct-pay basis, concierge practices provide patients with immediate, unrestricted access to physicians, bypassing the delays often associated with traditional insurance networks.
Key features of concierge healthcare include:
- 24/7 global access to certified doctors for urgent and routine needs.
- Customized health plans based on genetics, medical history, and personal health goals.
- Emphasis on preventive measures and wellness strategies.
- Seamless coordination across specialists and diagnostic services.
This model is especially attractive to corporate clients and busy professionals seeking premium, hassle-free healthcare. As the private sector continues to innovate, the role of concierge medicine is expected to expand, shaping the future of personalized health management.
Trends and the Future of Private Healthcare
The private healthcare sector is experiencing rapid growth driven by technological advancements and shifting patient expectations. Key trends shaping its evolution include:
Technology-Driven Personalized Healthcare
Emerging innovations such as wearable devices, genetic testing, and AI analytics are transforming diagnostics and treatment plans. These tools enable more precise, individualized care, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
Virtual Care and Telemedicine
Telehealth services are increasingly integrated into private healthcare offerings, allowing remote consultations, online diagnostics, and continuous health monitoring. This expansion makes healthcare more accessible and convenient, especially for international or remote patients.
Artificial Intelligence in Health Management
AI technologies are supporting proactive health management by identifying early risk factors, monitoring health metrics in real-time, and optimizing personalized treatment strategies. This integration promises more efficient, predictive, and preventative healthcare models.
Conclusion
Private healthcare systems offer faster access, personalized treatments, and access to innovative technologies, making them a compelling choice for many. However, considerations around costs and coverage limitations are important factors to weigh. Understanding the structure, benefits, and future trends of private healthcare empowers individuals and organizations to make better health decisions.
Integrating private services with concierge care options enhances the overall healthcare experience, providing 24/7 access, tailored health plans, and seamless coordination. For busy professionals seeking premium health management, exploring membership plans like those at WorldClinic can be a strategic move to prioritize well-being and long-term health.
FAQs About Private Healthcare Systems
1. Is private healthcare worth it?
For individuals who prioritize personalized attention, rapid access, and advanced treatments, private healthcare often justifies its higher costs. This investment can be particularly valuable for high-net-worth individuals and corporate executives seeking premium services.
2. Why might private healthcare be considered superior?
Private healthcare typically provides quicker access to specialists, a wider selection of providers, and access to innovative treatments. These features make it a preferred choice for those seeking efficiency and high-quality care, although affordability remains a key consideration.
3. Can Americans access private healthcare?
Yes. The US offers a broad array of private healthcare options, including concierge practices, private insurance plans, and employer-sponsored benefits. Patients usually select providers and funding sources based on their preferences and needs.
4. What proportion of the US population utilizes private healthcare?
Approximately 65% of Americans are covered by private insurance plans. However, many treatments and services may still require out-of-pocket payments, underscoring the importance of understanding individual coverage details.
5. Who primarily funds private healthcare?
Funding generally comes from a combination of out-of-pocket expenses, employer-sponsored plans, and private insurance coverage, with the specific mix varying based on individual circumstances and coverage choices.





