Clarifying the Role of Key Participants in Healthcare Decision-Making
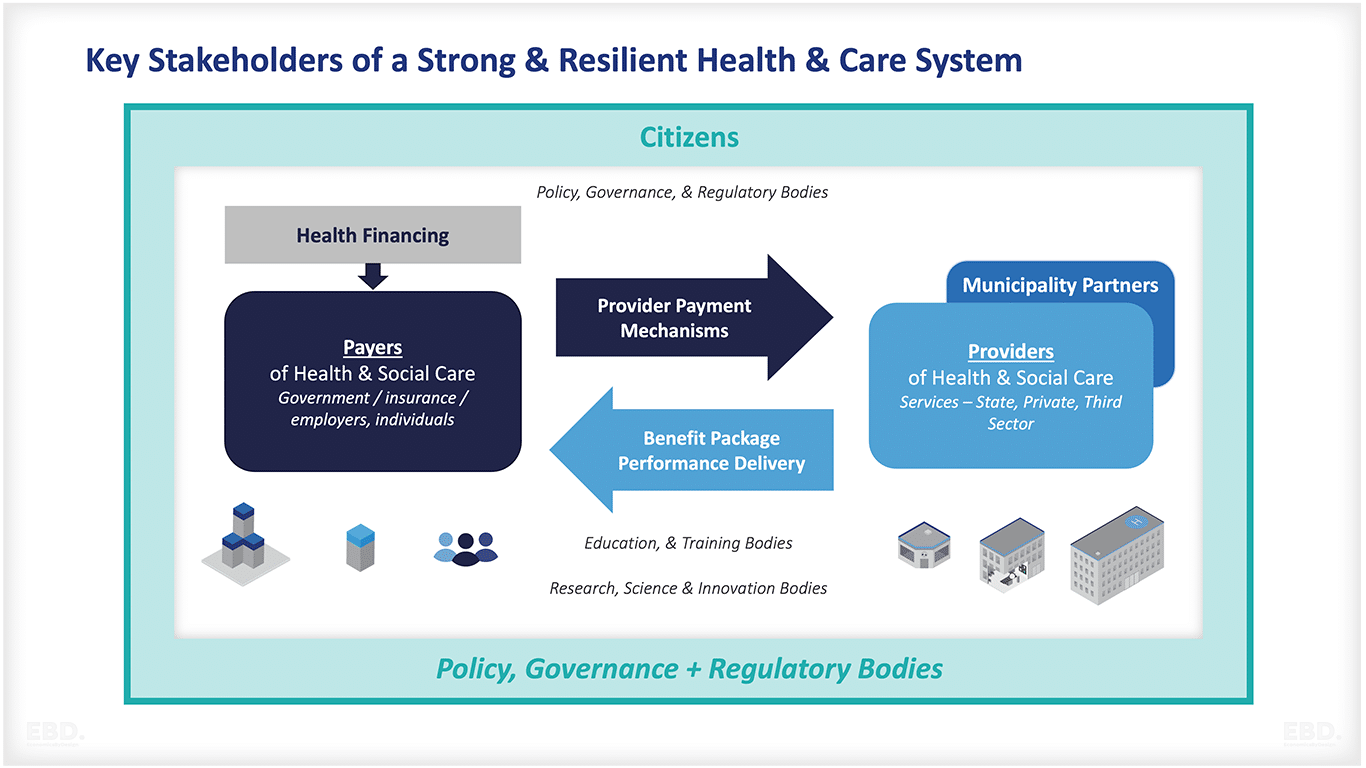
Understanding who influences healthcare policies and patient outcomes is essential for navigating the complex medical landscape. Stakeholders encompass a wide array of individuals and organizations, each with distinct interests and responsibilities that collectively shape the delivery of care. Recognizing these roles helps patients and practitioners appreciate the interconnected nature of healthcare systems, and how collaboration or conflict among these parties can directly impact the quality, accessibility, and efficiency of services. From patients and clinicians to insurers and government bodies, each stakeholder’s influence is vital in creating a responsive and effective healthcare environment.
Understanding Stakeholders in Healthcare
Stakeholders are the key players involved in the planning, implementation, and evaluation of healthcare services. Their interests, priorities, and actions significantly influence healthcare policies, resource allocation, and patient experiences. For a comprehensive understanding, it is helpful to explore some primary examples:
Patients: As the primary recipients of healthcare, patients’ experiences and feedback are crucial. Their perspectives can drive improvements in service quality and patient safety. Engaged patients often participate in decision-making processes, advocating for their needs and preferences. The increasing use of patient satisfaction surveys and feedback mechanisms exemplifies how patient voices can lead to tangible changes in healthcare delivery.
Healthcare Providers: Medical professionals—including doctors, nurses, therapists, and specialists—are responsible for delivering care and ensuring treatment efficacy. Their clinical expertise and insights into patient needs influence treatment guidelines and care protocols. Providers often collaborate in developing clinical standards that aim to improve outcomes and ensure safety.
Insurance Companies: These organizations determine what treatments and services are covered and how much is reimbursed. Their decisions on coverage policies directly impact patient access to necessary care and influence provider workflows. For example, reimbursement rates and coverage limits can incentivize or constrain certain medical interventions, affecting the overall efficiency of the system.
Government Agencies: Federal, state, and local authorities establish regulations that govern healthcare practices. They set standards for safety, quality, and privacy, and oversee public health initiatives. Agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) establish policies that influence healthcare delivery on a national scale, ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Each of these stakeholders contributes a unique perspective, which can sometimes lead to conflicts or synergies. For instance, while patients prioritize access and quality, providers focus on effective care, and insurers seek cost containment. The interplay among these groups determines policy decisions and the overall patient experience. Their collaboration—or lack thereof—can either enhance or hinder healthcare outcomes, highlighting the importance of understanding these relationships.
Types of Stakeholders
Different groups within the healthcare system influence decision-making processes in distinct ways. Recognizing the various types of stakeholders provides insight into how healthcare policies are shaped and implemented.
Patients and Their Families
Patients are at the core of healthcare systems. Their firsthand experiences and satisfaction levels influence quality improvement initiatives. Feedback collected through surveys or direct communication often prompts hospitals and clinics to revise procedures or enhance patient-centered care. Family members also play a vital role in advocating for loved ones, helping ensure that treatment plans align with patient preferences and needs.
Healthcare Providers
Doctors, nurses, specialists, and other frontline staff are the operational backbone of healthcare delivery. Their clinical judgments and day-to-day interactions with patients inform treatment standards and protocols. Engaging healthcare providers in policy discussions ensures that guidelines are practical and grounded in real-world experience.
Insurers and Payers
Insurance entities and other payers make critical decisions regarding coverage options, reimbursement rates, and formulary management. Their policies influence which treatments are accessible and affordable for patients. For instance, a comprehensive understanding of what is demographic data in healthcare can reveal how demographic factors influence insurance coverage decisions and resource distribution.
Interesting:
- Clarifying the role of npp in healthcare privacy and provider responsibilities
- The role of clinical decision support systems in modern healthcare
- Navigating the role of clinical decision support systems in modern healthcare
- The significance of hipaa key benefits and its role in modern healthcare
- Clarifying the role of personally identifiable information in healthcare privacy
Government and Regulatory Bodies
Government organizations oversee compliance with health laws and regulations designed to protect public health. They establish standards for safety, privacy, and quality care—such as those under HIPAA—and enforce them through inspections and penalties. Agencies like the CDC and FDA play integral roles in setting policies that affect every aspect of healthcare delivery.
Community Organizations
Local and non-profit organizations often address specific public health issues within communities. They provide health education, outreach, and support services tailored to underserved populations. These groups help bridge gaps between formal healthcare systems and community needs, fostering healthier environments and more equitable access.
Importance of Stakeholders in Healthcare
The collective influence of stakeholders drives continual improvements in healthcare quality and policy. Their diverse interests and contributions are vital in fostering a system that is responsive and patient-centered.
Enhancing Patient Care
Input from stakeholders directly impacts care quality. For example, patient feedback can lead to the implementation of new protocols that reduce wait times or improve communication. Family involvement often ensures that care plans are personalized, respecting individual preferences and cultural values. Engaged stakeholders contribute to safer, more effective healthcare environments.
Driving Policy Changes
Active participation by various stakeholders can catalyze significant policy reforms. When insurers, providers, and advocacy groups collaborate, they can influence legislation to expand coverage, improve access, or address emerging health challenges. For example, efforts to improve mental health services have gained momentum through stakeholder advocacy, illustrating the power of collective action.
Challenges Faced by Stakeholders
Despite their crucial roles, stakeholders encounter numerous obstacles that hinder optimal collaboration and decision-making.
Communication Barriers
Effective communication is often impeded by medical jargon, language differences, and technological gaps. For example, patient understanding of complex treatment options can be limited if explanations are not tailored appropriately. Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings, non-compliance, or dissatisfaction, highlighting the need for clear dialogue and health literacy initiatives.
Conflicting Interests
Divergent priorities among stakeholders can create tensions. Patients may seek affordable, accessible care, while insurers aim to control costs, and providers focus on delivering high-quality treatment. These conflicting aims can delay treatments or restrict available services, emphasizing the importance of negotiation and compromise. Recognizing these conflicting interests allows stakeholders to develop strategies that balance these priorities effectively.
Understanding these dynamics and challenges is essential for fostering collaboration and ensuring that healthcare systems serve the best interests of all involved parties. For more insights into technological advances transforming healthcare, including virtual reality in medicine perspectives and features, stakeholders must stay informed about emerging tools and innovations.
Note: This content has integrated relevant external links to authoritative sources, providing additional context and depth for readers seeking to understand the multifaceted roles within healthcare decision-making.





